Young Adults
Curious about STIs? We have answers for you!
We’ve dedicated this site to the eradication of wondering, second-guessing, and general puzzlement when it comes to chlamydia and gonorrhea. It’s not a popular subject, but talking about sexual infections is the best way to prevent them. The more you know about the diseases – the risks, the symptoms, the prevention techniques – the better you’ll know how to avoid encountering one.
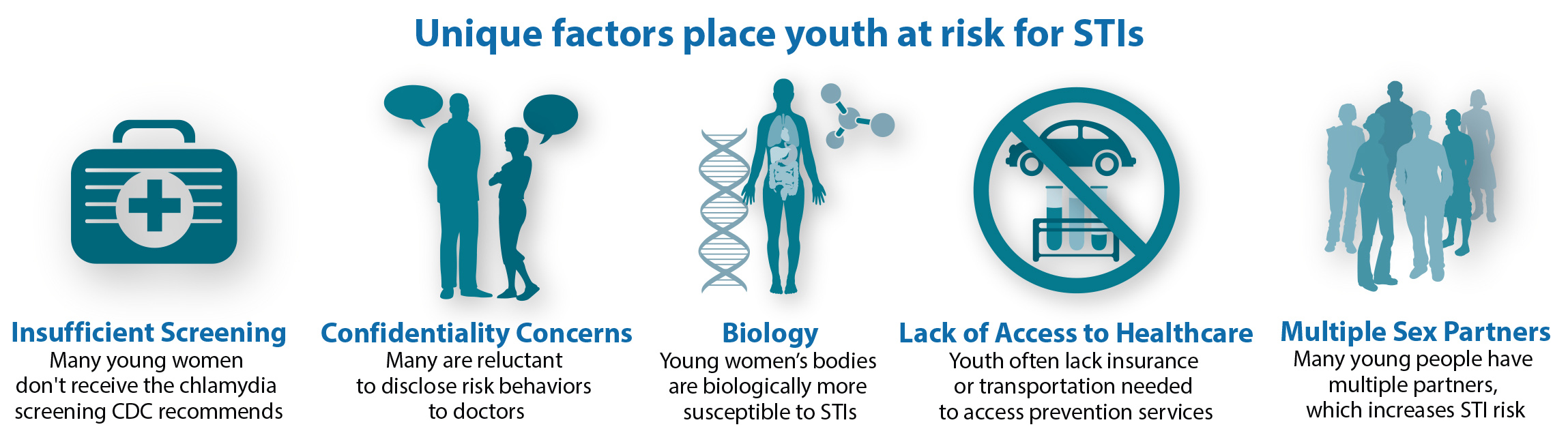
Youth Have Unique Risk Factors
Did you know that 15-24-year-olds account for half of all new STIs? It’s true. Much of this is due to unique factors that place youth at risk:
Things To Consider Before Having Sex
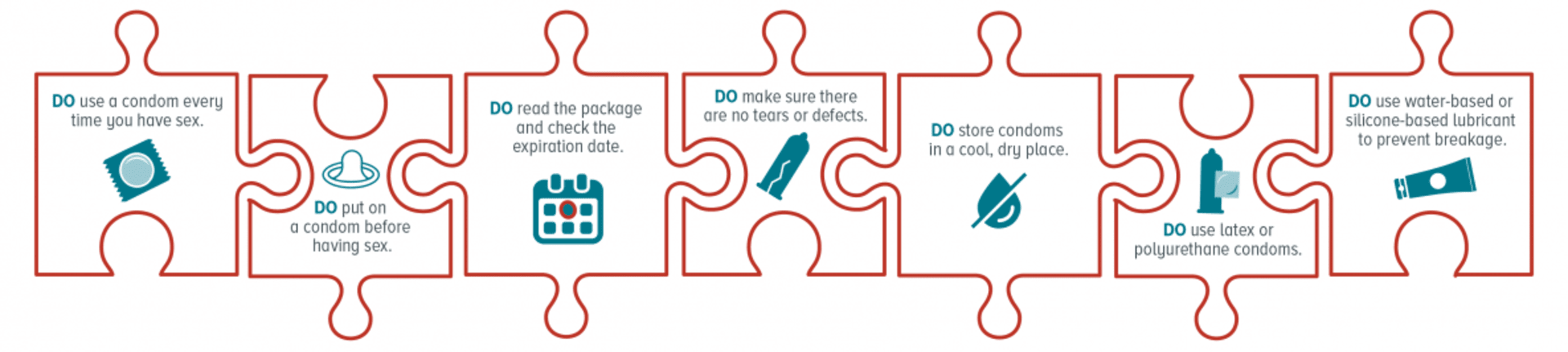
There are many opens in a new tabthings to consider before having sex. Although you may be curious about sex, or have a strong attraction to someone, it is important to understand the risks of having sex without taking the proper precautions. Abstinence is the only way to fully prevent against STIs and unplanned pregnancy. If you do decide to have sex, you and your partner should both be tested for STIs beforehand. Then ensure that you and your partner both know opens in a new tabhow to use a condom properly from start to finish.
Condom Locator
The condom locator below can be used to find free or low cost condoms near you. Condoms can also be found at some local health departments or purchased at most grocery stores, gas stations, and pharmacies.
Where To Get Tested
There are many places throughout Utah that offer friendly, confidential low/no cost STI tests. To find a testing location near you, please see the Resource Guide below.
Who To Talk To
If ever you have any questions, reach out and talk to either a parent or another trusted adult. It is worth it to be honest and voice your questions and concerns. You will be glad you did. It is also important to be open and honest with your healthcare providers to ensure your health and safety.
Utah’s Minor Consent Law Concerning Confidentiality of Treatment and Investigations of STIs
- Utah Code Section 26B-7-213 opens in a new tab allows a minor to consent to medical care or other services by a hospital or clinic under a licensed physician if they are infected with an STI or suspected to be in need of testing or treatment for an STI. This CAN be done without the consent of the parent.
- All chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV cases are reportable. These investigations are done at a Local Health Department. These investigators legally CANNOT tell parents about their child’s STI without the child’s permission.
Learn More
Visit EduMed’s website to learn more about STIs and staying safe during intimacy. opens in a new tab
Want to Know More?
Visit our question and answer page to see the answers to commonly asked questions about sexual health and STIs.